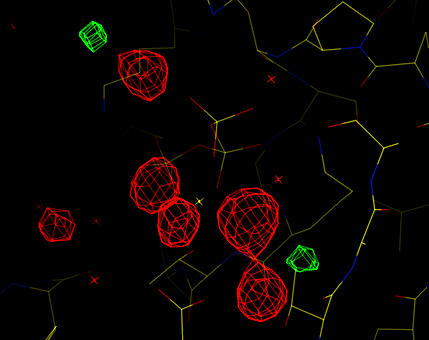
Missing waters around the magnesium ion are clear.
The model statistics are checked (as at the start of refinement) in order to check the model geometry and fit to the experimental diffraction data. In this example the CNS task file model_stats_final.inp is used to analyse the model geometry and diffraction statistics:
cns_solve < model_stats_final.inp > model_stats_final.out [2 minutes]
The output listing file (model_stats_final.list) contains a variety of information which is self-explanatory. Important things to note are:
R-values:
=================================== summary ==================================
resolution range: 500 - 1.9 A
R-values:
initial r= 0.3787 free_r= 0.3728
after B-factor and/or bulk solvent correction r= 0.2535 free_r= 0.2846
R-values versus resolution:
================================= R-values ===================================
=======> R-values with |Fobs|/sigma cutoff= 0.0
Test set (test = 1):
#bin | resolution range | #refl |
1 4.09 500.01 529 0.2456
2 3.25 4.09 439 0.2512
3 2.84 3.25 538 0.2974
4 2.58 2.84 514 0.3214
5 2.39 2.58 517 0.3041
6 2.25 2.39 484 0.3032
7 2.14 2.25 456 0.3091
8 2.05 2.14 461 0.3490
9 1.97 2.05 393 0.3855
10 1.90 1.97 382 0.3589
Working set:
#bin | resolution range | #refl |
1 4.09 500.01 4660 0.2028
2 3.25 4.09 4764 0.2345
3 2.84 3.25 4636 0.2786
4 2.58 2.84 4532 0.2777
5 2.39 2.58 4460 0.2809
6 2.25 2.39 4336 0.2710
7 2.14 2.25 4185 0.2912
8 2.05 2.14 3993 0.3152
9 1.97 2.05 3754 0.3212
10 1.90 1.97 3412 0.3525
This distribution of R-values is reasonable - there is no dramatic increase in R-value (in particular free R-value) as resolution increases. If there were resolution shells with R-values significantly higher than the rest this might indicate possible problems with the data processing (ice rings for example). However, the R-values indicate the fit to the experimental data and should not be manipulated by removing data - in particular by the use of sigma cutoffs to exclude weak data.
The overall geometry:
rmsd bonds= 0.010768 with 7 bond violations > 0.05 rmsd angles= 1.30473 with 6 angle violations > 8.0 rmsd dihedrals= 21.92063 with 3 angle violations > 60.0 rmsd improper= 0.83026 with 9 angle violations > 3.0
These overall statistics are acceptable, but it is necessary to check the outlying angle and improper deviations in the detailed geometry analysis (below).
The geometry in detail:
================================= geometry =================================== =======> bond violations (atom-i |atom-j ) dist. equil. delta energy const. (N 100 SD |N 100 CE ) 1.670 1.791 -0.121 2.475 170.066 (N 182 SD |N 182 CE ) 1.642 1.791 -0.149 3.791 170.066 (N 184 CG |N 184 SD ) 1.745 1.803 -0.058 1.709 512.111 (N 184 SD |N 184 CE ) 1.643 1.791 -0.148 3.741 170.066 (N 239 SD |N 239 CE ) 1.579 1.791 -0.212 7.630 170.066 (N 243 SD |N 243 CE ) 1.694 1.791 -0.097 1.606 170.066 (N 247 SD |N 247 CE ) 1.739 1.791 -0.052 0.456 170.066 =======> angle violations (atom-i |atom-j |atom-k ) angle equil. delta energy const. (N 28 N |N 28 CA |N 28 C ) 99.397 111.200 -11.803 10.519 247.886 (N 58 N |N 58 CA |N 58 C ) 119.986 111.200 8.786 5.829 247.886 (N 68 N |N 68 CA |N 68 C ) 100.627 111.200 -10.573 8.441 247.886 (N 129 N |N 129 CA |N 129 C ) 102.275 111.200 -8.925 6.015 247.886 (N 162 N |N 162 CA |N 162 C ) 121.455 111.800 9.655 8.831 310.948 (N 197 N |N 197 CA |N 197 C ) 99.437 111.200 -11.763 10.448 247.886 =======> improper angle violations (atom-i |atom-j |atom-k |atom-L ) angle equil. delta energy const. period (N 40 N |N 40 CA |N 40 CD |N 39 C ) -5.434 0.000 5.434 0.899 100.000 0 (N 62 N |N 62 CA |N 62 CD |N 61 C ) 4.523 0.000 -4.523 0.623 100.000 0 (N 140 N |N 140 CA |N 140 CD |N 139 C ) -3.584 0.000 3.584 0.391 100.000 0 (N 143 CA |N 143 N |N 143 C |N 143 CB ) 38.771 35.264 -3.506 2.808 750.000 0 (N 143 N |N 143 CA |N 143 CD |N 142 C ) -3.454 0.000 3.454 0.363 100.000 0 (N 162 N |N 162 CA |N 162 CD |N 161 C ) 5.476 0.000 -5.476 0.913 100.000 0 (N 195 CA |N 195 N |N 195 C |N 195 CB ) 38.272 35.264 -3.008 2.067 750.000 0 (N 249 N |N 249 CA |N 249 CD |N 248 C ) 5.758 0.000 -5.758 1.010 100.000 0 (A 1 PG |A 1 O1G |A 1 O2G |A 1 O3G ) -30.095 -35.000 -4.905 5.496 750.000 0 =======> dihedral angle violations (atom-i |atom-j |atom-k |atom-L ) angle equil. delta energy const. period (N 182 CB |N 182 CG |N 182 SD |N 182 CE ) 164.604 90.000 -74.604 9.295 5.000 2 (A 1 O1A |A 1 PA |A 1 O5* |A 1 C5* ) -13.796 180.000 -166.204 0.000 0.000 0 (A 1 O5* |A 1 C5* |A 1 C4* |A 1 C3* ) -83.679 180.000 -96.321 0.000 0.000 0
Specific problems with the model geometry can be identified here. The systematically longer bond lengths for the methionine SD CE bond may seems strange. However, they are caused by the use of the experimental phases in the refinement. These phases were generated for the protein with selenomethionine. The selenium carbon bond for (SE CE) is longer and the force constant for the SD CE bond is low (allowing the bond length to deviate from the expected values).
After analysis of the geometry and fit to the experimental data electron density maps should be checked. Cross-validated, sigma-A weighted, phase combined 2Fo-Fc and difference maps are calculated:
cns_solve < model_map_final_1fofc.inp > model_map_final_1fofc.out [30 seconds]
cns_solve < model_map_final_2fofc.inp > model_map_final_2fofc.out [1 minute]
If you have mapman installed, you can use the command
map_to_omap *.map
to convert the CNS maps to a format which can be read into
O. In O, enter @omac to read in the current
model and map.
Analysis of the difference map shows that some ordered water molecules are still missing. These can be placed either manually or by further rounds of automated water picking.
 |
| Cross-validated, phase combined Sigma-A weighted difference map (red is +4 sigma, green is -4 sigma). Missing waters around the magnesium ion are clear. |